Dust Collection Systems
A dust collection systems is designed to eliminate particulate contaminants from the air in production facilities, workshops, and industrial settings. It works by directing the air through a series of airtight filters to remove dust and other particles.
Dust Collection Systems
After filtration, the clean air is either expelled outdoors or recirculated, provided it meets the required emission standards.
With increasing environmental concerns, dust collection systems have become essential for industries that generate significant dust and gas emissions. Manufacturers must comply with stringent government regulations and demonstrate the effectiveness of their systems, ensuring they meet EPA, NFPA, and MSHA standards.
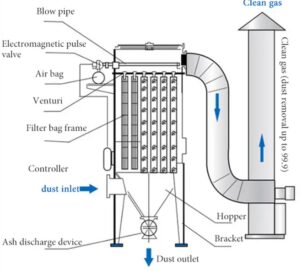
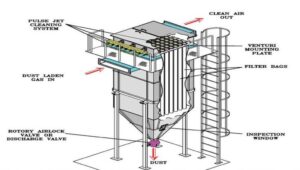
How a Dust Collection System Works
In simple terms, a dust collection system is built to remove particulates from the air generated during operations. This brief description oversimplifies the complexity and innovation involved in designing and creating an effective system for capturing harmful contaminants.
A dust collection system typically consists of several key components: a blower, dust filter bag, cleaning system, receptacle, ductwork, and mechanisms for capturing particulate matter. Common types of dust collection equipment include fabric filter baghouses, inertial separators (also known as mechanical cyclones), cartridge collectors, wet scrubbers, and electrostatic precipitators. Baghouse dust collectors are the most widely used due to their high efficiency, often achieving 99%.
The types of pollutants removed vary by industry. Dust collector manufacturers design and develop equipment tailored to meet the specific needs of different environmental conditions.
Dust collection systems include ductwork for drawing in air, an air purifier, and a receptacle. The configuration of these basic elements varies depending on the type of system.
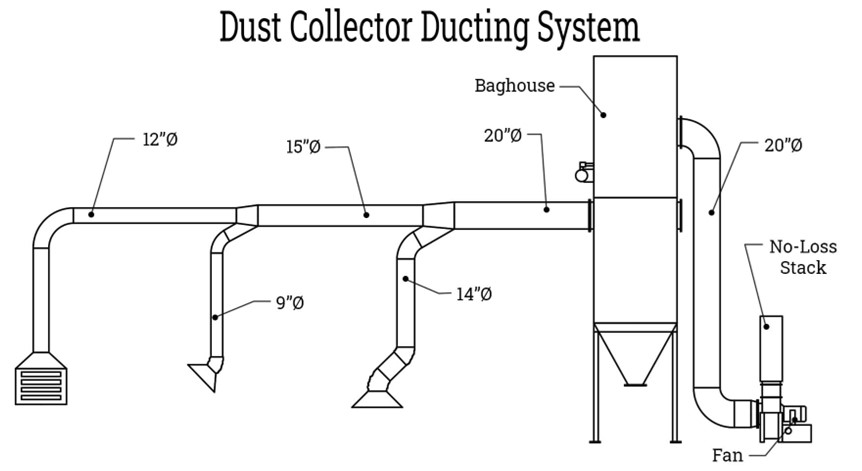
Dust Collection Ductwork
While the design of ductwork may appear straightforward, it must be meticulously planned to ensure the system functions properly. The pipe size is determined by factors such as the tool size, air requirements, pipe length, number of machines being serviced, and the types of particulates being extracted. The ductwork size varies throughout the system and is responsible for channelling the air collected by fans and collectors.
Fans or Blowers
Although a fan or blower may have a simple design within a dust collection system, several factors must be taken into account. The primary consideration is the volume of air that needs to be moved, measured in cubic feet per minute (CFM). Additionally, static pressure throughout the system must be assessed, along with other variables such as temperature, airborne substances, and moisture levels.
The blower or fan is a critical element in a dust collection system since it is the mechanism that pulls the contaminated air into the ductwork away from the workplace and sends it to the filtration and cleaning systems. The basic types of blowers are centrifugal and axial. The centrifugal type has wheels in the housing, while the axial type has propellers.

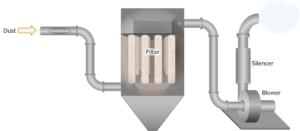
Dust Filter (Filter Bag)
The dust filter is the component responsible for cleaning the air in a dust collection system. There is no single standard for dust collection filters. Essentially, the blower draws air from the area into the filter, which removes particulates from the air. The air-to-cloth ratio refers to the amount of air that passes through each square foot of the filter. A lower ratio indicates a higher quality and efficiency of the filtration system.
Structure and working principle of bag filter
In short, the structure of a bag filter is the same as that of a vacuum cleaner. This system filters the gas containing dust using a filter (filter bag), and only the clean gas is discharged.
Filter materials include fibres such as polyester, heat-resistant nylon, and glass fibres, and are selected depending on the properties of the gas and dust.
Dust Filter Cleaning System
As particulates accumulate on the filter surface, the filtration system in a dust collection setup can become clogged and filled. Various methods are used to clean filters, some of which require shutting down the system. For systems that must run continuously, alternative cleaning methods that allow operation to continue are necessary.
An on-demand dust collection system features a controller equipped with a pressure sensor to monitor the filter’s static differential. This system measures the pressure difference between the clean and dirty air plenums. When the differential becomes too high, the controller triggers a diaphragm valve to release compressed air into the filter, removing the accumulated particles. This process is known as pulse jet baghouse or pulse jet dust collection, which is a common method for controlling particulate air pollution.
A Magnehelic gauge tracks the pressure, while a Photohelic gauge, connected to the timer board, interacts with the pulse cleaning system.
Other systems trigger an alarm to alert operators when a significantly high pressure is reached. Most systems, regardless of whether they are on-demand or not, are equipped with control devices that notify operators of collection failures or drops in pressure across the filter.

Bag filter maintenance
Filter bag is a consumable item. If the filter is damaged, dust will leak out and it will need to be replaced. The lifespan varies depending on the application and type of dust, making it difficult to determine when it is time to replace it.
In recent years, dust meters (dust monitors) have been increasingly installed on the secondary side (gas discharge side) of bag filters to constantly monitor the dust leak amount. In fact, simply constantly monitoring the amount of dust leakage (dust concentration) with a dust meter can help optimize timing of replacing filter cloth and reduce maintenance costs.
Trouble caused by filter (filter bag) breakage and its countermeasures
Problems caused by dust leakage
When bag filters are used for many years, the filters become damaged and deteriorate due to the friction of powder particles. As you can imagine, if the filter breaks, the collected powder will be released into the atmosphere, but it can also cause damage to the equipment.
For example, if a filter is broken, dust will leak out, and the leaked dust will adhere to the inside of the blower to cause corrosion. Due to this corrosion, loads are given on various parts of the blower, and in some cases, it may even stop. It is important to understand possible problems and take countermeasures before such a situation occurs.
Countermeasure: Monitoring dust concentration
Traditionally, working environment measurements based on manual analysis methods have been the mainstream, but there are periods when monitoring is not possible using only this method, and there is a possibility that leaks may go unnoticed. To avoid this, it is necessary to constantly monitor the dust concentration using a dust meter (dust monitor).

